Introduction
As expected, the COVID-19 pandemic, now thankfully coming to a close, radically shifted the very tectonic plates of the marketing industry. From marketer optimism to a strategic change from defense to offense, backend changes to skyrocketing internet sales (remember how crazily difficult it was to find hand sanitizer at first?), the very industry responsible for business production and outreach will never be the same.
The content marketing industry segment is no exception to this shift. However, the net effect of the pandemic on content marketing was, by and large, a positive one. Having always been an essential key feature for businesses’ internet presence and advertising, content marketing became even more important for businesses during these three years. As internet usage soared and internet sales hit all-time highs, content marketing became the backbone for business sustainability.
The Impact of the Pandemic on Content Marketing – A Deeper Analysis
Let’s first define content marketing to contextualize it within the marketing industry and differentiate it from other types of marketing. Broadly defined, content marketing, according to the Content Marketing Institute, is:
“A strategic marketing approach focused on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and retain a clearly defined audience — and, ultimately, to drive profitable customer action.”
Content marketing includes all media content – from videos to images to music to writing – that helps bolster a company’s brand and propagate its products and services. There are several ways in which content marketing has changed throughout the pandemic. We list them categorically below.
Changes in Buyer Behavior
One of the most prominent ways in which content marketing changed during the pandemic is in correlation with increased internet activity and media consumption that went along with the near-vanishment of the physical consumer space.
With increased online activity came upshifts in purchasing behavior. One statistic indicates that media consumption in the US went up 215% between March 2019 and March 2020. American consumers also spent $211.5 billion on e-commerce during the second quarter of 2020, a 31.8% increase from the previous quarter.
Adapting Content Marketing Strategies
Content marketing strategies shifted during the pandemic, for sure. There was an adaptation process in which companies produced more pandemic-related content. There are millions of examples, such as The Bank of Guam’s “Stop Covid, Spread Love.”
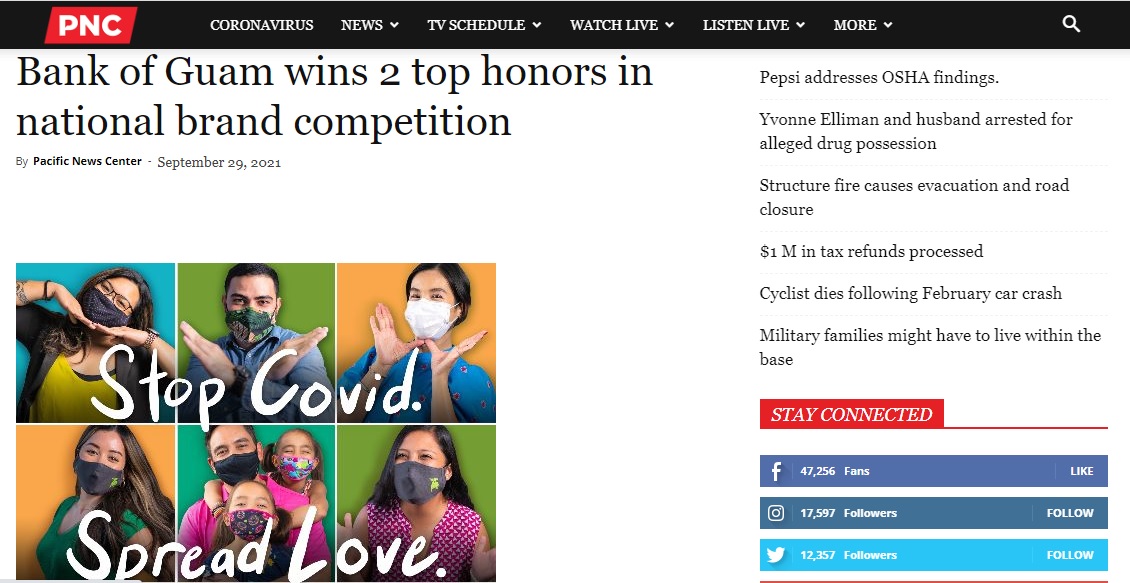
What digital channels did businesses use to accomplish their marketing goals? P2P was much less of an option, so many businesses that had relied on such methods took advantage of increased social media content to disseminate their products and services. These media included Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, and many others.
Building brands amid a worldwide pandemic also inspired content marketers to empathize with consumers. While some took advantage of this empathy to make aggressive sales, those who humanized the process built more trust with their customers and, from this, more durable relationships.
Measuring the Impact of the Pandemic on Content Marketing
There are three main tools that you can utilize to look back at the pandemic and establish correlations between consumer behavior and content marketing trends: analytics tools, tracking engagement, and analyzing user feedback.
Analytics tools are forms of application software that compile data illustrating trends of multiple business systems and house it in a repository, where it is then reviewed and analyzed. During the pandemic, such tools looked at consumer behavior, growth and growth/diminishment rates patterns, and general market trends. The role of analytics showed that to drive personalization and promote growth, it was critical to identify markets to see where and how fast consumers were engaging with digital media and buying products and services.
Businesses also tracked engagement to contextualize their progress. Staggering statistics showed that consumer engagement spiked during the pandemic, including a 28% increase in the frequency with which they engaged with interactive media, resulting in an overall 94% increase in engagement.
Lastly, analyzing user feedback was seriously impactful, as well. In one poll, 39% of social media users said they spent more time on social media than before the pandemic.

The Impact of the Pandemic on SEO
Here, we’ll explore the impact of the pandemic on the search engine optimization side of content marketing.
Changes in Search Behavior
The pandemic radically affected search behavior. To demonstrate this, in 2020, Google published data designed to assist marketers in being more helpful to their businesses’ customers.
In the research, Google uncovered five key search behaviors that had changed dramatically during 2020 alone:
- Assembling critical information: searching for key instructions on how to get basic needs met during the pandemic, such as “Where to buy hand sanitizer” or “How to fit a mask properly.” These searches were based on acknowledging the new normal and encouraged marketers to deliver credible, facts-based material that demonstrated consumer empathy in authentic and genuine ways. This aided in relatability and customer loyalty for the most successful enterprises.
- Forging new connections: The massive surge in popularity of video platforms like Zoom helped people worldwide nurture friendships in radically new ways and make new friends through MMPGs and online study sessions despite the necessary social distancing.
- Adapting to routine changes: Isolation certainly upended many people’s typical 9-5 workday. Google, in its research, encouraged marketers to deliver effective communications strategies in content that promotes general well-being and health.
- Giving credit to ordinary heroes: Due to the everyday bravery of frontline workers, humanity came together, and there was a proliferation of searches for items like “Thank our healthcare workers.”
- Actions toward self-care and care for others: From physical to mental and emotional health, in 2020, searches were up for how to come together as a world’s people and take care of each other. These were the best of times; these were the worst of times…
On top of these content-driven search trends, there was also an increase in voice searches during the pandemic to stem infection that could result from tactile transmission. China led the way here, but US technologies have since caught up and pioneered new ways of communicating via voice, such as WoeBot Health and Suki.

Adapting SEO Strategies
To optimize for voice searches, American, European, and Chinese companies all invested in voice AI as the pandemic forced the world’s populace to rethink its relationship with technology to reduce disease transmission and communicate quickly across platforms. Voice AI allowed doctors to take notes in long form as their plates were overloaded, and they could offload data onto an app like Suki. Consumer usage of Alexa, Siri, and Google, in general, went way up, not only because of the desire to avoid tactile transmission by keeping off of more surfaces but also because of the isolation at home.
The utilization of local SEO was also a key factor during the pandemic. Local businesses had to compete with tech juggernauts like Amazon and others and, as a result, developed clever ways to distribute their products and services using local SEO.
This included creating pandemic-relevant and engaging content in many ways. For example, establishing a clear COVID-19 health policy was radically important, as was reorganizing website data based on such a policy, including updates on product availability and helping local communities survive through branding messages that encouraged “banding together.” Particularly successful companies also used Google Business analytics and profile optimization tools.
Measuring the Impact of the Pandemic on SEO
Similar to how businesses and their marketers measured the impact of the pandemic on content marketing, these entities also used analytics tools, tracked search engine rankings, and analyzed user feedback to optimize their enterprises.
Firstly, search engines like Google and Bing were active in publishing well-documented data about SEO trends through their various analytics tools. Companies could thus use the Rich Results Test Tool, Structured Data Testing Tool, and others to optimize their branding and marketing practices.
The ability to track search engine rankings was another critical avenue for businesses to optimize their SEO marketing strategies. This is where the verdict was that search engines could’ve done a better job publishing these results more equitably, steadily, and consistently. These search engines prioritized information about the pandemic but favored certain communities and organizations that left others in the dust. Still, results were published, and companies did take advantage of this highly prized information.
Lastly, companies could engage in user feedback to optimize SEO practices. Avenues like Google Reviews and customer services chats allowed companies to expand their reach and maximize SEO based on real-time user data and feedback.
Conclusion
As you can see, the pandemic upended and fundamentally redefined content marketing and SEO practices for virtually all businesses across the globe, from small to large, local to inter/multinational.
From a content marketing perspective, digital media consumption increased exponentially, allowing companies to adjust their products and services and how they were marketed. This also included new brand-building strategies and cultivating more empathy, care, and concern with users, particularly around COVID-19-related topics.
From an SEO vantage point, brand messaging became fundamentally tailored to new modes of thinking and learning, from facilitating the forging of new and nurturing old relationships for people using online meeting applications and software to developing innovations for Voice AI to decrease tactile transmission.
From these data and studies come a slew of tips and strategies for your business to adapt, now in the post-pandemic phase. Concrete strategies like empathy and the encouragement of wellness and basic needs can help you steer customers toward more human-centric practices, products, and services that induce unification over division, coming together over standing apart. Such messaging based on the newfound vulnerability post-pandemic will be one of the most critical content marketing and SEO strategies your business can adapt to.
FAQs
1. How has the pandemic affected the marketing industry?
This is a broad question requiring a real investment of time to understand, but we can encapsulate it by indicating that a shift toward health, wellness, empathy, and basic needs, as well as the cultivation of human connectedness, have all shifted the marketing industry toward skyrocketing engagement with digital media, internet sales, and internet technologies.
2. What changes in human behavior did we observe over the pandemic?
We saw a trend toward increased searches related to adjusting to the “new normal” of staying at home and working from home, health and wellness, care and concern for others, including praising ordinary heroes such as frontline workers, and a move toward Voice AI to decrease transmission of the virus potentially resulting from shared surfaces.
3. How can I measure the impact of the pandemic on my content marketing efforts?
To measure this impact, use analytics tools, track engagement, and analyze user feedback.
4. How has the pandemic affected SEO?
Changes in user search behavior toward health, wellness, security, basic needs, COVID-19-related facts and practices, and increased security and safety all formed the basis for one of the significant shifts in SEO practices for marketers during the pandemic. In addition, local businesses took advantage of SEO to compete with more prominent tech companies and establish more personal and customer-centered brand awareness.
5. How can I measure the impact of the pandemic on my SEO efforts?
You can use analytics tools, track search engine rankings, and analyze user feedback.